7 hours ago
By Yolande Knell, BBC Middle East correspondent

 EPA
EPAUltra-Orthodox Jews in full time study have been exempt from conscription since the beginning of the state
When Israel’s ultra-Orthodox or Haredi Jewish community gathers in force you realise just how large it is.
Thousands of men and boys dressed in black and white are crammed into the streets of Mea Shearim – which is the heart of the ultra-Orthodox community – in Jerusalem for an angry protest against the military draft.
It is the latest demonstration since the Supreme Court’s historic ruling that young Haredi men must be conscripted into the Israeli military and are no longer eligible for significant government benefits.
Young men who are full-time students in Jewish seminaries, or yeshivas, tell me that their religious lifestyle is in jeopardy. They believe that their prayers and spiritual learning are what protects Israel and the Jewish people.
“For 2,000 years we’ve been persecuted, and we’ve survived because we’re learning Torah and now the Supreme Court wants to remove this from us, and it will cause our destruction,” says Joseph.
“Going to the army will make a frum – religious Jew – not religious anymore.”
“The draft does not help militarily. They don’t want us Haredim, us orthodox Jews, they don’t need us,” another student tells me, withholding his name as he does not have his rabbi’s permission to give an interview.
“They’re just gonna give us some dirty job there. They’re there to make us not Orthodox no longer.”

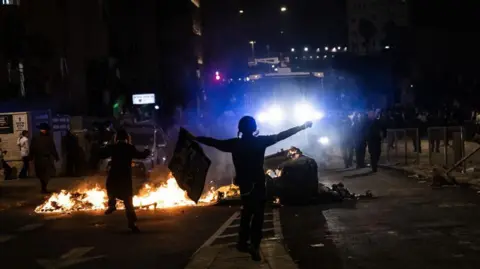 Anadolu via Getty Images
Anadolu via Getty ImagesClashes erupted in Jerusalem between Israeli police and ultra-Orthodox Jews over the weekend
For decades, there has been controversy over the role of the ultra-Orthodox in Israeli society. From a small minority, the community is now a million-strong, making up 12.9% of the population.
Ultra-Orthodox parties have often acted as kingmakers in Israeli politics, giving support to successive governments headed by Israel’s prime minister Benjamin Netanyahu, in return for continuing the draft exemption and hundreds of millions of dollars for their institutions.
This has been a long-standing cause of friction with secular Jewish Israelis who mostly do compulsory military service and pay the largest share of taxes. But the issue has now come to a head at the most sensitive time as the army faces unprecedented strain following its longest ever war in Gaza, and a possible second war with Hezbollah in Lebanon.
“My son has already been in the reserves for 200 days! How many years do you want him to do? How are you not ashamed?” demanded Mor Shamgar as she berated Israel’s national security adviser at a recent conference in Herzliya.
Her exasperated rant about her son – serving as a tank commander in southern Israel – was widely shared on social media.
With army leaders complaining about a shortage of military manpower, Ms Shamgar – who says she has previously voted for the prime minister’s party – believes that the government has “handled the situation very poorly,” putting its own political survival ahead of national interests on the draft issue.
“Netanyahu and his gang made a major judgement mistake on thinking they can dodge it,” she tells me. “Because once you enforce on half the population that you have to go to the army, you cannot enforce that the other half will not go to the army. It’s not even secular versus religion. I see it as an equality issue. You can’t make laws that make half a population, second grade citizens.”
Earlier this year, a survey by the Israel Democracy Institute indicated that 70% of Israeli Jews wanted to end the blanket exemptions from military service for the ultra-Orthodox.
Despite earlier threats, so far ultra-Orthodox parties have not left the governing coalition over army conscription. Attempts continue to push forward an older bill – once rejected by Haredi leaders – that would lead to partial enlistment of their community.
At an ultra-Orthodox synagogue in Jerusalem, men of different ages are draped in their prayer shawls gathering for the morning service. Their conservative way of life is based on a strict interpretation of Jewish law and customs.
So far, just one Israeli army battalion, Netzah Yehuda, was set up specifically to accommodate ultra-Orthodox demands for gender segregation with special requirements for kosher food, and time set aside for prayers and daily rites.


Rabbi Yehoshua Pfeffer has called on the army to improve its relationship with the ultra-Orthodox community
But an ultra-Orthodox rabbi who works on issues of integration and is on the board of an NGO that supports the battalion, believes more compromises are possible and that a new Haredi brigade should be formed.
“It’s up to the Haredim to come to the table and say, we’re ready for real concessions, we’re ready to step out of our traditional comfort zone and do something proactive in finding the right framework that will allow more Haredi to serve,” says Rabbi Yehoshua Pfeffer.
He suggests thousands of young ultra-Orthodox men who do not currently do full-time Torah study – finding themselves unsuited to academic rigours – should be encouraged to join the army like other Jewish Israelis their age.
For the Israeli military to live up to its reputation as “the People’s Army,” Rabbi Pfeffer also calls on it to do more to build trust and improve its relationship with his community. “There are a lot of accommodations needed, but they’re not rocket science,” he comments.
So far, the process of implementing the ultra-Orthodox draft appears gradual.
More than 60,000 ultra-Orthodox men are registered as yeshiva students and have been receiving an exemption from military service. But since last week’s Supreme Court ruling, the army has only been told to draft an additional 3,000 from the community, in addition to about 1,500 who already serve. It has also been told to devise plans to recruit larger numbers in coming years.
Back in Mea Shearim, after nightfall there are some protesters who take an extreme position, throwing stones at the police and spreading out in Jerusalem to attack the cars of two ultra-Orthodox politicians who they feel have let them down on military conscription.
Historically, this is an insulated section of society that resists change but now amid rising public pressure in Israel and the possibility of widening war, change appears unavoidable.

